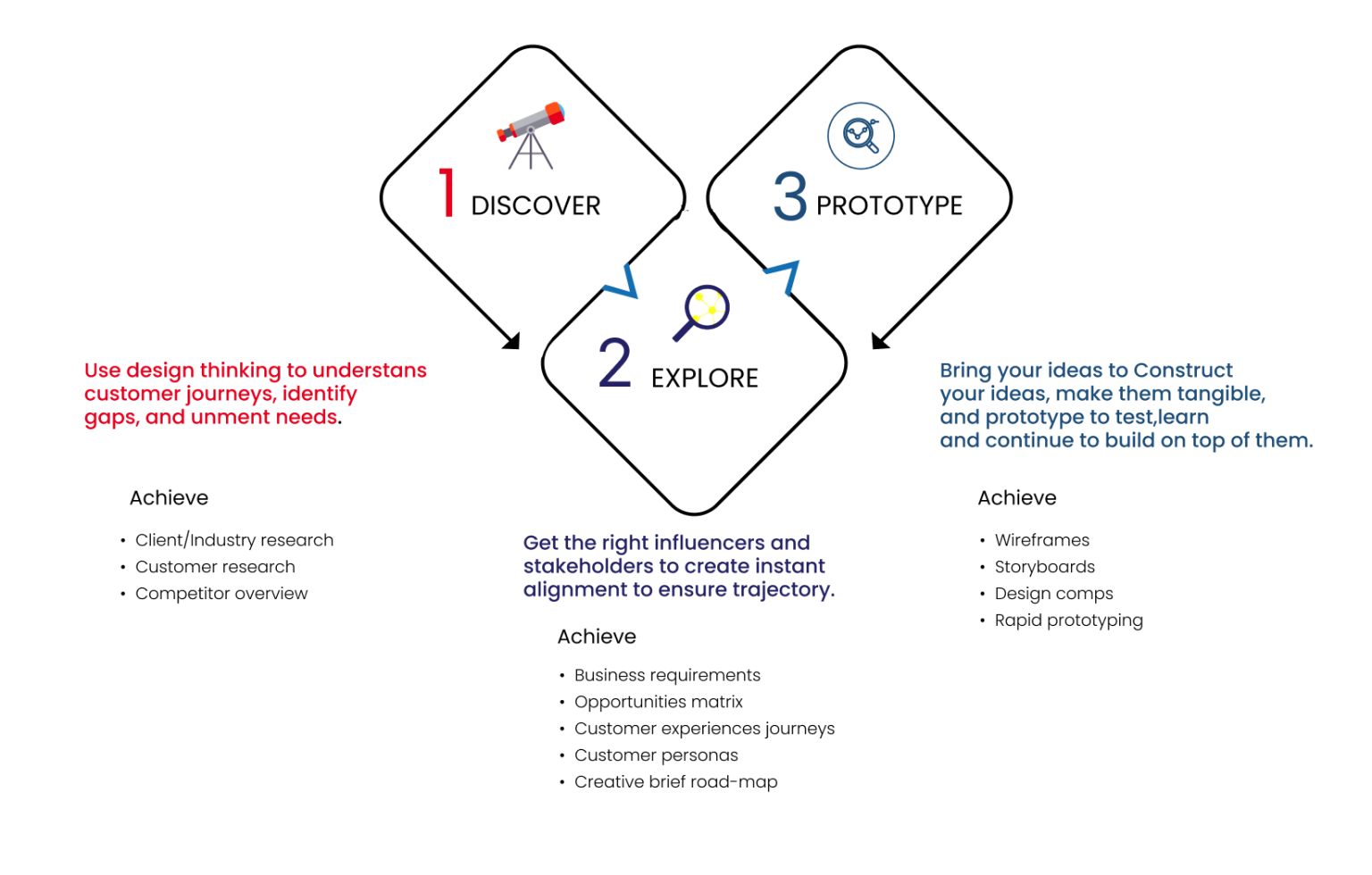
Our Offerings
Define
Integrating deep learning to take in what is customer’s needs & wants and by doing extensive research in customer’s product/service and their competitors, defining the desired prototype is attainable.
Decide
To create an optimal ground for tangible results, a versatile workflow, feedback incorporation, and utilising resources at the right time with the right person bring the prototype to its fruition.
Deliver
Fabricating your concepts into a functional prototype through a solidified process, to evaluate, assimilate and elevate through and throu
Our Approach
- Modelling concepts to process swiftly
- Transparent and persuasive approach
- A well-defined methodology with applicable resources
- Enhancing progressively based on critiques
- Instant and Quality Delivery
Latest Thinking
Frameworks that help make critical product innovation and management decisions
- The article draws insights from Gartner’s elaborate survey involving product leaders and their teams across the world, on making successful Product innovation and management decisions so as to drive growth.
- Gartner comes up with a multi-pronged methodology called Product Management Framework to boost the innovation and management of the product throughout its development cycle.
Gartner’s Product Management Framework is built around five key areas called the decision points.

1) Product planning:
The product planning phase involves the following steps:
Knowing the market needs: Identifying who the target client base is and collecting inputs from the existing customers to understand what prospects and future, the customer is looking for?
Size of the market opportunity:Estimating the size of potential markets and trends affecting these markets.
Analyze the competitors: By evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of competitors, understanding their offerings & services stack.
Creating a product strategy: Establishing a vision based on an analysis of the market environment as well as the company’s competencies.
2) Product development:
Owing to its technical complexity, this is the most challenging of all the tasks that product managers perform. This phase involves:
Evolving the product: Aims at building products that meet customer needs.
Differentiate the product: Understand what differentiates your product in the market.
Develop customer experience: Involves pricing models, business models, and delivery models & partnerships.`12 Involves how fast the team can make it to the market.
3) Product introduction:
This is a critical step in commercializing the product, the purpose of this phase is to
Prepare the product for the public, in other words, the developed product is prepared in order to be sold and marketed to the public.
To see beyond the release phase: so as to make sure the product sustains commercial visibility in the long run.
The product introduction phase involves:
Managing the market: Here, the team decides what sales model best fits your product launch.
Deliver Value: involves balancing the business & technical features so as to deliver the value of that product.
Pricing & Packaging of the product: The product is priced & packaged into offerings.
Working with the marketing team: The product team interacts with the product marketing team to come up with marketing plans.
4) Product Life Cycle Management:
This phase involves the full life cycle of a product, right from the planning, introduction, and growth saturation, to its decline. The more microscopic analysis of the product life cycle phase involves:
Grow Revenue: How the product grows in revenue, and how can it be displaced in case of disruptions.
Innovate further: how to future innovate & evolve the product.
Best Practices: How to apply the best practices around the product (like product recalls, end of life, critical events regarding the product).
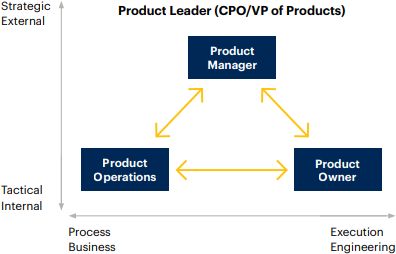
5) Product leadership
The purpose of product leadership is to create efficient organizational structures by recruiting & developing talented resources and creating efficient communication channels across the company to address product development challenges.
Gartner points out five key disciplines that make product managers, the masters of product leadership.
- Build a strong team.
- Measure the business-unit performance
- Implement new approaches
- Share a new product management toolkit.
- Align the product management team with the company
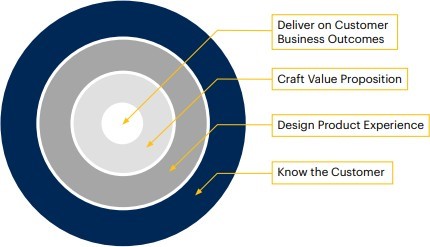
How Technology Product Leaders Can Drive Revenue Growth
The post-pandemic world is witnessing a revolutionary change in the ways people do business. Accelerated technology innovation and changing patterns of buying coupled with new business models have added to the complexity of how technology providers need to think about the operations of an organization.
The article gives a brief overview of Gartner’s Leadership vision to leaders and their teams, based on data-driven research as to, where to focus-inorder to yield an outstanding performance, hence drive revenue generation.
Key challenges Technology Product Managers face:
- Lack of data-based decisions
• Most operations suffer from inadequacy of data, with their insights confined to sales and other financial records.
• To tackle this, product management leaders should begin to capitalize on the new trend of near-real-time usage and behavioural data. - Changing buyer’s behaviour
As markets increasingly become global with intensifying competition, product management leaders and their teams need to identify new ways to make their products and services stand out. - Focusing on the most important thing
The Gartner’s product management survey 2020, revealed that product managers split their tasks across at least 10 activities like tactical, strategic and collaborative with no single task getting at least 15% of estimated allocations.
Actions to address the challenges
Encourage hypothesis-based problem solving and decision-making culture among product managers and discourage the preconceived use of data.
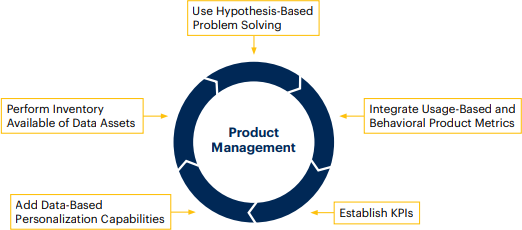

Develop outcome-driven guidelines for the entire product development lifecycle (planning. development, validation). Prioritize providing compelling customer experiences and product investments.

Achieve specialization, to lead complex responsibilities and deliver valuable solutions to customers’ real-time problems.
As engines of growth and deliverers of continuous product management, product management organizations and their leaders and teams must grow, in terms of specialization. It is through specialization, that the team can handle complex responsibilities and offer quick & valuable solutions to customers’ real-time problems.

5 Steps to Validate New High-Tech Product Planning
Planning a hi-tech product is a challenging task, as it is almost uncertain if the customers embrace the new product’s offerings or not. A typical product planning process starts from the ‘ product ideation’ phase. Once the ideation sustains the internal scrutiny, momentum builds.
Ideation Phase
Before the validation process, the new product idea should be defined with enough clarity to understand the following:
- What is the product and what does it do?
- Who is the product’s target customer?
The hypothesis for the above-mentioned cases is tested and refined through a validation process. If the new product idea sustains the validation process, the project is said to have won the confidence of stakeholders in its probability of market success.
Validation Process
1) Sharing the concept
Involves pitching the idea to a bunch of people within the professional network of the team coupled by the team, attending meetups and other events that offer an opportunity to interact with other technology professionals.
The purpose of which is to refine the idea through repeated discussion. The derive the critical feedback
2) Analyzing the Market
In this phase, the new product’s potential competitive environment is evaluated. The team performs a fact-finding on things like, what will be the category of the product, the existing alternatives, their shortcomings and how the product being developed stands out in the face of alternatives etc so as to help make informed decisions regarding their disruption.
3) Value-Assessment
The next step is to estimate the business value that the new product offers to customers. Financial value is integral in B2B technology purchase decisions, and the validation phase serves as a pre-checkpoint to ensure that the product being developed is worth & compelling when viewed from the financial lens.
4) Validating the product planning hypotheses with target buyers
In this step, the product planning hypothesis is put to validation by the real buyers. The purpose of which is not to pitch a pre-sale of the product, but to confirm and expand the team’s understanding of buyer needs and their willingness to bid on a purchase.
The challenge in this step is to identify the right target buyers for the validation process. In other words, the validation is to be obtained from the hierarchy, responsible for championing the
purchase of the product from the end of the target customer organization, as the validation should come from real buyers.
5) Release minimum viable product
A minimum viable product is a developmental technique where the new product is introduced in the market with minimum/basic features, but enough to catch the attention of the consumers The purpose of this is to prove to the customer before both the parties fully commit to the idea of sell & buy.
Credit
The article draws inputs from Gartner’s ‘Guidelines for Validating Tech-Product Planning’. Gartner Inc is technological research and consulting firm, every year, it identifies leading technology trends crucial to business growth and possesses the potential to be the game changers to organizations.
Our Ecosystem
We extend our technology and business capabilities through a powerful ecosystem of market leaders and innovators, from the largest platform companies to startups and niche players.


